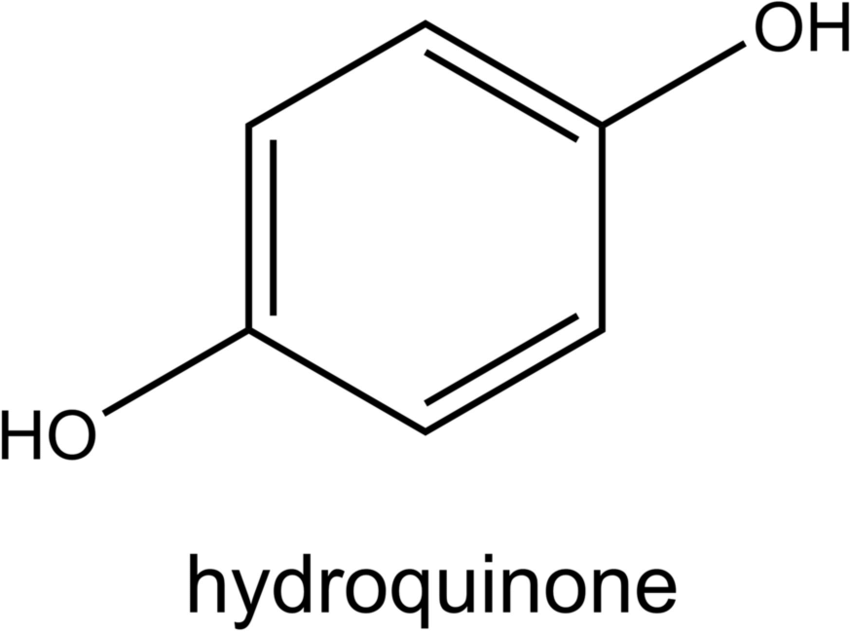
Lightening Dark Spots with Hydroquinone
Hydroquinone has been used in the beauty industry for decades to lighten dark spots on your face from hyperpigmentation, age spots, or freckles. It comes in a non-prescription strength up to 2% concentration in serums or creams that is available over the counter for home treatment, and up to 4% for prescription strength. The effectiveness of hydroquinone working as a skin lightening agent resulted in its popularity, but there has been some controversy surrounding its adverse effects.
Hydroquinone Basics 101:
What is Hydroquinone?
Although hydroquinone can be found in nature, it is often created in a lab. Hydroquinone is phenol derivative with antioxidant properties used in many skin lightening products as a topical treatment for hyperpigmentation. There are two types that you can get either over the counter and doctor prescribed strength. Classified as a drug in the US, it is only available by prescription in four percent concentrations and over the counter in two percent doses.
What Is It Used For?
It is helpful in treating different forms of skin conditions such as melasma, freckles, dark spots resulting from skin aging, post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation from psoriasis and eczema, and darker skin caused by acne scars. The synthetic compound works as a skin bleaching agent promising to brighten dark patches.
How Does Hydroquinone Work?
Topical hydroquinone breaks down and minimizes melanin production in melanocytes by inhibiting tyrosinase, the enzyme needed to make melanin. It temporarily blocks your body from making melanin, a type of pigment that gives your skin its color. In cases of hyperpigmentation, more melanin is present due to an increase in melanocyte production.
How To Use Hydroquinone?
Consistent use of hydroquinone cream will give maximum results in treating uneven skin tone and brown spots. It is important to do a patch test by applying a thin layer on the inside of the forearm. Check the test area for allergic reactions, irritation, or any other possible side effects. Discontinue hydroquinone use if irritation persists or sensitive skin severely itches. If your skin can tolerate hydroquinone treatment, you can safely add it to your skincare routine. Apply a thin film over the affected areas and evenly across the skin making sure that it is completely absorbed. With hydroquinone therapy treated areas, using sunscreen daily is important. Sun exposure can have the reverse effect by worsening hyperpigmentation.

How Long Should Hydroquinone Be Used?
Hydroquinone therapy should not be used for more than 6 months consecutively. Dermatologists usually prescribe hydroquinone cream to be used cyclically because the results of skin lightening products on age spots, hyperpigmentation, melasma, and acne scars are not permanent. It is possible to keep hyperpigmentation at bay and from reemerging by have a skin care routine that includes the right dosage and adminstration of hydroquinone cream.
How Long Does It Take Hydroquinone To Work?
Although topical use of hydroquinone is proven effective as a skin-lightening product, results will not be noticed overnight. Hydroquinone treatment usually reveals lighter skin tone in about four weeks although some skin conditions may require a longer treatment plan.
Side Effects Of Hydroquinone Treatment
Generally, hydroquinone is well tolerated. In some instances, mild burning, stinging, redness, dryness, blistering, skin cracking, or darkening of the skin may occur. Sunscreen of at least SPF30 is necessary to prevent skin from getting darker again. If side effects persist, stop using hydroquinone. Severe allergic reactions to hydroquinone are uncommon but are possible, including rash, itching/swelling, severe dizziness, or trouble breathing.
Is Hydroquinone Safe?
In some parts of the world, hydroquinone has been banned, questioning the safeness of its use. The mutagenic and carcinogenic potential of this chemical in animals has raised concerns on the effects it has on humans. Hydroquinone is FDA-approved, and there aren't any research studies or clinical evidence to suggest that there is any [human] harm.
Recent Posts
-
Hyaluronic Acid Injections
Hyaluronic Acid Injections: What to Know & Non-Invasive Alternatives That Actually Work In the p …Jun 17th 2025 -
Kojic Acid Creams
My Kojic Acid Journey: How One Ingredient Transformed My Skin (And the Best Kojic Acid Creams to Try …Jun 11th 2025 -
LightStim vs. Omnilux
LightStim vs. Omnilux: My Real LED Skincare Results & Which One I Recommend LED light therapy&nb …Jun 3rd 2025